Distributive property
In abstract algebra and formal logic, the distributive property of binary operations generalizes the distributive law from Boolean algebra and elementary algebra. In propositional logic, distribution refers to two valid rules of replacement. The rules allow one to reformulate conjunctions and disjunctions within logical proofs.
For example, in arithmetic:
- 2 ⋅ (1 + 3) = (2 ⋅ 1) + (2 ⋅ 3), but 2 / (1 + 3) ≠ (2 / 1) + (2 / 3).
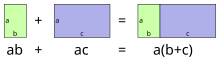
On the left-hand side of the first equation, the 2 multiplies the sum of 1 and 3; on the right-hand side, it multiplies the 1 and the 3 individually, with the products added afterward. Because these give the same final answer (8), multiplication by 2 is said to distribute over the addition of 1 and 3. Since one could have put any real numbers in place of 2, 1, and 3 above, and still have obtained a true equation, multiplication of real numbers distributes over addition of real numbers.
Definition[edit]
Given a set S and two binary operators ∗ and + on S, the operation * :
is left-distributive over + if, given any elements x, y and z of S,
is right-distributive over + if, given any elements x, y, and z of S,
- and
is distributive over + if it is left- and right-distributive.[1]
Notice that when ∗ is commutative, the three conditions above are logically equivalent.
Meaning[edit]
The operators used for examples in this section are the binary operations of addition () and multiplication () of numbers.
There is a distinction between left-distributivity and right-distributivity:
- (left-distributive)
- (right-distributive)
In either case, the distributive property can be described in words as:
To multiply a sum (or difference) by a factor, each summand (or minuend and subtrahend) is multiplied by this factor and the resulting products are added (or subtracted).
If the operation outside the parentheses (in this case, the multiplication) is commutative, then left-distributivity implies right-distributivity and vice versa.
One example of an operation that is "only" right-distributive is division, which is not commutative:
In this case, left-distributivity does not apply:
The distributive laws are among the axioms for rings (like the ring of integers) and fields (like the field of rational numbers). Here multiplication is distributive over addition, but addition is not distributive over multiplication. Examples of structures in which two operations are mutually related to each other by the distributive law (e. g., they distribute over each other) are Boolean algebras such as the algebra of sets or the switching algebra.
Multiplying sums can be put into words as follows: When a sum is multiplied by a sum, multiply each summand of a sum with each summand of the other sum (keeping track of signs) then add up all of the resulting products.
Examples[edit]
Real numbers[edit]
In the following examples, the use of the distributive law on the set of real numbers is illustrated. When multiplication is mentioned in elementary mathematics, it usually refers to this kind of multiplication. From the point of view of algebra, the real numbers form a field, which ensures the validity of the distributive law.
- First example (mental and written multiplication)
During mental arithmetic, distributivity is often used unconsciously:
Thus, to calculate 6 ⋅ 16 in one's head, one first multiplies 6 ⋅ 10 and 6 ⋅ 6 and add the intermediate results. Written multiplication is also based on the distributive law.
- Second example (with variables)
-
- Third example (with two sums)
-
- Here the distributive law was applied twice, and it does not matter which bracket is first multiplied out.
- Fourth Example
- Here the distributive law is applied the other way around compared to the previous examples. Consider
- Since the factor occurs in all summands, it can be factored out. That is, due to the distributive law one obtains
Matrices[edit]
The distributive law is valid for matrix multiplication. More precisely,
for all -matrices and -matrices , as well as
for all -matrices and -matrices . Because the commutative property does not hold for matrix multiplication, the second law does not follow from the first law. In this case, they are two different laws.
Other examples[edit]
- Multiplication of ordinal numbers, in contrast, is only left-distributive, not right-distributive.
- The cross product is left- and right-distributive over vector addition, though not commutative.
- The union of sets is distributive over intersection, and intersection is distributive over union.
- Logical disjunction ("or") is distributive over logical conjunction ("and"), and vice versa.
- For real numbers (and for any totally ordered set), the maximum operation is distributive over the minimum operation, and vice versa: max(a, min(b, c)) = min(max(a, b), max(a, c)) and min(a, max(b, c)) = max(min(a, b), min(a, c)).
- For integers, the greatest common divisor is distributive over the least common multiple, and vice versa: gcd(a, lcm(b, c)) = lcm(gcd(a, b), gcd(a, c)) and lcm(a, gcd(b, c)) = gcd(lcm(a, b), lcm(a, c)).
- For real numbers, addition distributes over the maximum operation, and also over the minimum operation: a + max(b, c) = max(a + b, a + c) and a + min(b, c) = min(a + b, a + c).
- For binomial multiplication, distribution is sometimes referred to as the FOIL Method[2] (First terms ac, Outer ad, Inner bc, and Last bd) such as: (a + b) · (c + d) = ac + ad + bc + bd.
- Polynomial multiplication is similar to that for binomials: (a + b) · (c + d + e) = ac + ad + ae + bc + bd + be.
- Complex number multiplication is distributive:
Propositional logic[edit]
| Transformation rules |
|---|
| Propositional calculus |
| Rules of inference |
| Rules of replacement |
| Predicate logic |
Rule of replacement[edit]
In standard truth-functional propositional logic, distribution[3][4] in logical proofs uses two valid rules of replacement to expand individual occurrences of certain logical connectives, within some formula, into separate applications of those connectives across subformulas of the given formula. The rules are
and
where "", also written ≡, is a metalogical symbol representing "can be replaced in a proof with" or "is logically equivalent to".
Truth functional connectives[edit]
Distributivity is a property of some logical connectives of truth-functional propositional logic. The following logical equivalences demonstrate that distributivity is a property of particular connectives. The following are truth-functional tautologies.
- Distribution of conjunction over conjunction
- Distribution of conjunction over disjunction
- Distribution of disjunction over conjunction
- Distribution of disjunction over disjunction
- Distribution of implication
- Distribution of implication over equivalence
- Distribution of disjunction over equivalence
- Double distribution
Distributivity and rounding[edit]
In practice, the distributive property of multiplication (and division) over addition may appear to be compromised or lost because of the limitations of arithmetic precision. For example, the identity ⅓ + ⅓ + ⅓ = (1 + 1 + 1) / 3 appears to fail if the addition is conducted in decimal arithmetic; however, if many significant digits are used, the calculation will result in a closer approximation to the correct results. For example, if the arithmetical calculation takes the form: 0.33333 + 0.33333 + 0.33333 = 0.99999 ≠ 1, this result is a closer approximation than if fewer significant digits had been used. Even when fractional numbers can be represented exactly in arithmetical form, errors will be introduced if those arithmetical values are rounded or truncated. For example, buying two books, each priced at £14.99 before a tax of 17.5%, in two separate transactions will actually save £0.01, over buying them together: £14.99 × 1.175 = £17.61 to the nearest £0.01, giving a total expenditure of £35.22, but £29.98 × 1.175 = £35.23. Methods such as banker's rounding may help in some cases, as may increasing the precision used, but ultimately some calculation errors are inevitable.
Distributivity in rings[edit]
Distributivity is most commonly found in rings and distributive lattices.
A ring has two binary operations, + and * (commonly), and one of the requirements of a ring is that ∗ must distribute over +. Most kinds of numbers (example 1) and matrices (example 4) form rings. A lattice is another kind of algebraic structure with two binary operations, ∧ and ∨. If either of these operations (say ∧) distributes over the other (∨), then ∨ must also distribute over ∧, and the lattice is called distributive. See also the article on distributivity (order theory).
Examples 4 and 5 are Boolean algebras, which can be interpreted either as a special kind of ring (a Boolean ring) or a special kind of distributive lattice (a Boolean lattice). Each interpretation is responsible for different distributive laws in the Boolean algebra. Examples 6 and 7 are distributive lattices which are not Boolean algebras.
Failure of one of the two distributive laws brings about near-rings and near-fields instead of rings and division rings respectively. The operations are usually configured to have the near-ring or near-field distributive on the right but not on the left.
Rings and distributive lattices are both special kinds of rigs, certain generalizations of rings. Those numbers in example 1 that don't form rings at least form rigs. Near-rigs are a further generalization of rigs that are left-distributive but not right-distributive; example 2 is a near-rig.
Generalizations of distributivity[edit]
In several mathematical areas, generalized distributivity laws are considered. This may involve the weakening of the above conditions or the extension to infinitary operations. Especially in order theory one finds numerous important variants of distributivity, some of which include infinitary operations, such as the infinite distributive law; others being defined in the presence of only one binary operation, such as the according definitions and their relations are given in the article distributivity (order theory). This also includes the notion of a completely distributive lattice.
In the presence of an ordering relation, one can also weaken the above equalities by replacing = by either ≤ or ≥. Naturally, this will lead to meaningful concepts only in some situations. An application of this principle is the notion of sub-distributivity as explained in the article on interval arithmetic.
In category theory, if (S, μ, η) and (S′, μ′, η′) are monads on a category C, a distributive law S.S′ → S′.S is a natural transformation λ : S.S′ → S′.S such that (S′, λ) is a lax map of monads S → S and (S, λ) is a colax map of monads S′ → S′. This is exactly the data needed to define a monad structure on S′.S: the multiplication map is S′μ.μ′S2.S′λS and the unit map is η′S.η. See: distributive law between monads.
A generalized distributive law has also been proposed in the area of information theory.
Notions of antidistributivity[edit]
The ubiquitous identity that relates inverses to the binary operation in any group, namely (xy)−1 = y−1x−1, which is taken as an axiom in the more general context of a semigroup with involution, has sometimes been called an antidistributive property (of inversion as a unary operation).[5]
In the context of a near-ring, which removes the commutativity of the additively written group and assumes only one-sided distributivity, one can speak of (two-sided) distributive elements but also of antidistributive elements. The latter reverse the order of (the non-commutative) addition; assuming a left-nearring (i.e. one which all elements distribute when multiplied on the left), then an antidistributive element a reverses the order of addition when multiplied to the right: (x + y)a = ya + xa.[6]
In the study of propositional logic and Boolean algebra, the term antidistributive law is sometimes used to denote the interchange between conjunction and disjunction when implication factors over them:[7]
- (a ∨ b) ⇒ c ≡ (a ⇒ c) ∧ (b ⇒ c)
- (a ∧ b) ⇒ c ≡ (a ⇒ c) ∨ (b ⇒ c)
These two tautologies are a direct consequence of the duality in De Morgan's laws.
Notes[edit]
- ^ Distributivity of Binary Operations from Mathonline
- ^ Kim Steward (2011) Multiplying Polynomials from Virtual Math Lab at West Texas A&M University
- ^ Elliott Mendelson (1964) Introduction to Mathematical Logic, page 21, D. Van Nostrand Company
- ^ Alfred Tarski (1941) Introduction to Logic, page 52, Oxford University Press
- ^ Chris Brink; Wolfram Kahl; Gunther Schmidt (1997). Relational Methods in Computer Science. Springer. p. 4. ISBN 978-3-211-82971-4.
- ^ Celestina Cotti Ferrero; Giovanni Ferrero (2002). Nearrings: Some Developments Linked to Semigroups and Groups. Kluwer Academic Publishers. pp. 62 and 67. ISBN 978-1-4613-0267-4.
- ^ Eric C.R. Hehner (1993). A Practical Theory of Programming. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 230. ISBN 978-1-4419-8596-5.
External links[edit]
| Look up distributivity in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- A demonstration of the Distributive Law for integer arithmetic (from cut-the-knot)



































No comments:
Post a Comment